Take The Next Step To Lasting Health
-
Sample Type: Blood
-
Age: 18+
-
HSA/FSA: Accepted
-
Collection Method: In person at our location
-
Results: 2-4 days from when your sample arrives at our lab
-
Test must be taken by purchaser
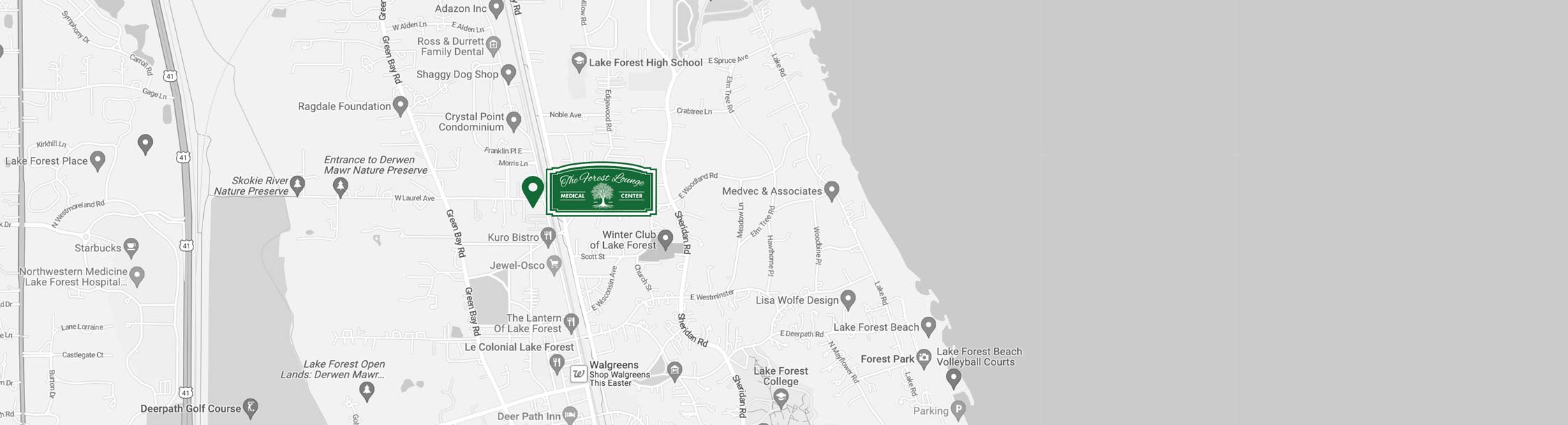
Functional Medicine Lake Forest IL
Treatment and Diagnosis in Lake Forest, Illinois
Functional Medicine is a personalized, systems-based approach to healthcare that focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of disease rather than just treating symptoms. Instead of asking “What drug matches the disease?” Functional Medicine practitioners ask, “Why is this happening in the first place?” It views the body as an interconnected system — not a collection of independent organs — and considers how factors like genetics, environment, lifestyle, and diet interact to influence long-term health and chronic illness. Patients often undergo advanced testing to evaluate inflammation, hormone imbalances, gut health, and nutrient deficiencies, allowing practitioners to create highly tailored wellness plans.
Many people are drawn to Functional Medicine because it empowers them to take a more active role in their health journey. It appeals especially to those who feel unheard or underserved by traditional medicine, where appointments are often brief and treatment can be symptom-focused or reliant on prescriptions. Functional Medicine emphasizes collaboration between patient and practitioner, longer consultations, and holistic strategies that incorporate lifestyle changes, nutritional support, stress reduction, and in some cases, natural supplementation. For those dealing with chronic conditions like fatigue, autoimmune disease, or digestive issues, the promise of treating the cause instead of chasing the symptoms is a powerful motivator.
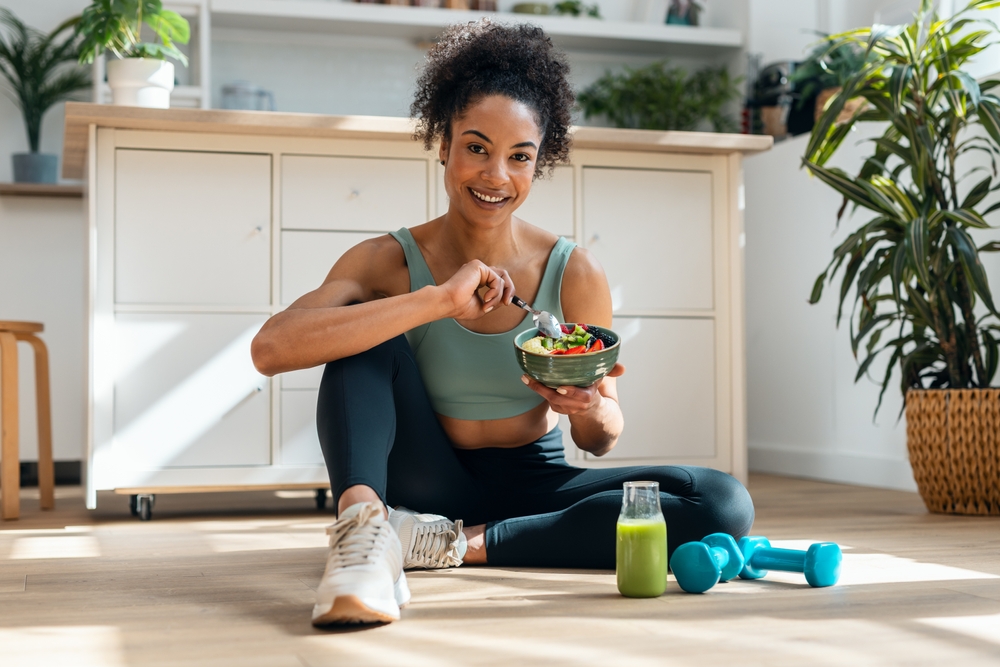
Micronutrient Test
Feeling low on energy? Find out if you’re low in these key vitamins and minerals.
This test measures the levels of six essential micronutrients in your blood, including three vitamins (vitamin D, vitamin B12 and folate) and three minerals (magnesium, iodine and zinc). Empower yourself with insights into your diet so you can make informed decisions about your nutrition and performance.

Preparation:
If you’re taking a supplement containing biotin (also called vitamin B7 or B8, vitamin H or coenzyme R), commonly found in products promoting nail, skin and hair health, we recommend that you wait at least 72 hours from your last dose before taking the test.
Micronutrient Test
Vitamin D
Our vitamin D test included in this panel measures the level of 25-hydroxy vitamin D in your blood. Vitamin D helps your body regulate calcium metabolism which in turn helps maintain healthy bones, control infections, reduce inflammation and more. Your skin produces vitamin D through sunlight exposure. Vitamin D is also found in foods such as fatty fish, mushrooms, egg yolks and fortified milks. When you’re deficient in vitamin D, you may experience symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness and depression. Additionally, you could become more prone to having fractures from falls if you have a vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin B12 Folate
Vitamin B12 plays an essential role in red blood cell formation, cell metabolism, nerve function and more. It’s found in foods such as nutritional yeast, plant-based milks and certain cereals. When you’re deficient in vitamin B12, you may experience symptoms like fatigue, weight loss and loss of appetite.
Iron
Calcium
Potassium
Pospherous
Vitamin E
Vitamin A
Folate
A natural form of vitamin B9, folate helps your body make new red blood cells and DNA, and it plays an important role in a fetus’s development. It’s found in foods such as leafy greens, beans, seafood, eggs and more. When you’re deficient in folate, you may experience symptoms like fatigue and weight loss.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a type of electrolyte—an electrically charged mineral—that helps your muscles, nerves and heart work properly. It’s found in foods such as legumes, nuts, seeds, greens and whole grains. When you’re deficient in magnesium, you may experience symptoms like fatigue, muscle cramps, numbness and/or tingling, an irregular heartbeat and more. Magnesium can impact the balance of other electrolytes, including potassium. It is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your test results and next steps.
Iodine
This trace mineral supports your thyroid function by helping to produce thyroid hormones. It’s found in foods such as iodized salt, milk, yogurt, cheese, shrimp, cod and tuna. When you’re deficient in iodine, you may experience symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, confusion and more.
Zinc RBC
Zinc is an essential trace mineral that supports numerous functions in the body, including red blood cell (RBC) health. Within RBCs, zinc plays a role in stabilizing cell membranes and protecting them from oxidative damage. It also supports the activity of enzymes involved in cellular metabolism and immune defense. Zinc is crucial for wound healing, DNA synthesis, and the proper functioning of taste and smell. In the context of red blood cells, zinc helps regulate iron metabolism and hemoglobin production, both of which are critical for oxygen transport. A deficiency in zinc can impair immune response, delay healing, and contribute to anemia-like symptoms due to its indirect role in supporting healthy RBC formation.
Copper
Copper is a vital trace mineral that plays a key role in red blood cell formation, iron metabolism, and energy production. It works closely with iron to help the body form hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Copper is also essential for maintaining healthy blood vessels, nerves, immune function, and connective tissue. Additionally, it acts as an antioxidant, helping protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. A deficiency in copper can lead to anemia, fatigue, weakened immunity, and even neurological issues due to its involvement in brain and nerve function.
Selenium
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that supports red blood cell (RBC) health primarily through its powerful antioxidant properties. It is a key component of enzymes like glutathione peroxidase, which protect RBCs from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. By preserving the integrity of red blood cell membranes, selenium helps maintain their function and lifespan. Selenium also supports immune function, thyroid hormone metabolism, and DNA synthesis. Although not directly involved in hemoglobin production, its role in reducing oxidative stress is critical in preventing premature RBC breakdown and supporting overall cellular health.
CoQ10
CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10) is a powerful antioxidant and essential compound that plays a critical role in cellular energy production. It’s found in every cell of the body, especially in high-energy organs like the heart, and helps generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the molecule that fuels cellular activity. In red blood cells and other tissues, CoQ10 protects cell membranes from oxidative stress, supporting their function and longevity. It also contributes to cardiovascular health by improving blood vessel function and reducing inflammation. As we age or under certain health conditions, natural CoQ10 levels may decline, making supplementation beneficial for energy, heart health, and overall cellular vitality.
Manganese
Manganese is an essential trace mineral that supports a wide range of biological functions in the body. It plays a key role in the formation of connective tissue, bones, and blood-clotting factors, as well as in the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, and cholesterol. Manganese also activates several important antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), which protects cells—especially red blood cells—from oxidative damage. It supports proper brain and nerve function and is involved in wound healing and energy production. Though needed in small amounts, manganese is vital for maintaining strong bones, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall cellular health.
Vitamin K1
Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, is essential for proper blood clotting. It activates proteins that allow your blood to coagulate, helping to stop bleeding after injuries. Without enough vitamin K1, even minor cuts could lead to excessive bleeding. Beyond clotting, it also supports bone health by helping to regulate calcium deposition—ensuring calcium is used where it’s needed in bones and not in soft tissues like arteries. Primarily found in leafy green vegetables, vitamin K1 plays a quiet but crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular and skeletal health.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function, helps the body absorb iron from plant-based foods, and plays a crucial role in collagen production—a protein needed for healthy skin, blood vessels, cartilage, and wound healing. It also protects cells from oxidative stress and helps regenerate other antioxidants in the body, like vitamin E. Because the body doesn’t store vitamin C, regular intake through diet or supplements is essential. A deficiency can lead to fatigue, weakened immunity, slower healing, and in severe cases, scurvy.
Omega 3
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that play a crucial role in heart, brain, and overall body health. They help reduce inflammation, lower triglyceride levels, support healthy brain function, and may reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Omega-3s also support eye health, improve joint flexibility, and may benefit mood and mental health. Since the body cannot produce omega-3s on its own, they must come from the diet — commonly through fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, or supplements like fish oil. Regular intake is important for maintaining healthy cell membranes and supporting many vital processes in the body.
CRP
CRP, or C-reactive protein, is a substance produced by the liver in response to inflammation in the body. A CRP test measures the level of this protein in your blood and is used to detect inflammation, which can be caused by infections, chronic diseases, or acute conditions like heart attacks. While it doesn’t show the exact location or cause of the inflammation, a high CRP level signals that something in the body is triggering an immune response. Doctors often use CRP testing to monitor conditions like autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disorders, or to assess heart disease risk when combined with other markers.
Chromium
Chromium is an essential trace mineral that plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels by enhancing the action of insulin, the hormone responsible for moving glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy. It also helps with the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, supporting overall energy production in the body. While the body only needs small amounts, chromium is important for maintaining normal glucose tolerance and may help improve blood sugar control, especially in people with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Additionally, chromium supports healthy cholesterol levels and may contribute to heart health.
Triglycerides
Total Cholesterol (LDL & HDL)
Total cholesterol is the overall amount of cholesterol in your blood, which includes both LDL and HDL cholesterol. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol, can build up on the walls of your arteries, leading to blockages, atherosclerosis, and an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol, helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream by carrying it back to the liver, where it can be broken down and eliminated. Together, these numbers give doctors an important snapshot of your heart health and help guide lifestyle or treatment recommendations.
Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)
VLDL (very low-density lipoprotein) is a type of lipoprotein that carries triglycerides through the bloodstream from the liver to tissues in the body. Like LDL (“bad” cholesterol), VLDL can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, heart disease, and stroke. VLDL is considered harmful mainly because it’s rich in triglycerides, and when these are broken down, they leave behind remnants that can further raise LDL levels. While VLDL is not always measured directly, it can often be estimated from triglyceride levels and gives additional insight into cardiovascular risk.
Glyco Panel
A glyco panel, often called a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test, measures the average blood sugar (glucose) levels over the past two to three months. It works by assessing how much glucose is attached to your hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. This test is commonly used to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes or to monitor how well someone with diabetes is managing their blood sugar over time. Unlike daily blood sugar checks, the HbA1c test gives a long-term view of glucose control, helping guide treatment decisions and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Simple Lipid Panel
A simple lipid panel is a blood test that measures the levels of fats (lipids) in your blood, helping assess your risk for heart disease. It typically includes four main components: total cholesterol, which is the overall amount of cholesterol in your blood; LDL cholesterol (often called “bad” cholesterol), which can build up in arteries and increase heart disease risk; HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol), which helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream; and triglycerides, which are fats that store unused calories and can also raise heart risk when elevated. This test helps doctors evaluate your cardiovascular health and guide lifestyle or treatment recommendations if needed.
Thyroid Panel
A thyroid panel with TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) is a blood test that checks how well your thyroid gland is working. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and signals the thyroid to make hormones like T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), which control your body’s metabolism, energy levels, heart rate, and temperature. The panel usually measures TSH along with free T3 and free T4 to give a full picture of thyroid health. High TSH levels can suggest an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), while low TSH can indicate an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). This test helps diagnose thyroid disorders and guide treatment to keep hormone levels balanced.
CMP + CBC
A Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) is a blood test that measures 14 different substances to evaluate your overall metabolic health. It provides important information about kidney and liver function, electrolyte and fluid balance, blood sugar levels, and protein and calcium levels. By analyzing components such as glucose, creatinine, BUN, sodium, potassium, ALT, AST, and others, a CMP helps detect conditions like diabetes, liver disease, kidney dysfunction, and dehydration. It’s a valuable tool for identifying internal imbalances before symptoms appear and is commonly used in routine health screenings or when diagnosing unexplained issues like fatigue or swelling.
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) measures the different types and quantities of cells in your blood. It looks at red blood cells (RBCs), which carry oxygen; white blood cells (WBCs), which fight infection; and platelets, which help with blood clotting. It also assesses hemoglobin, hematocrit, and various red blood cell indices (like MCV, MCH, and RDW) to evaluate the size, quality, and oxygen-carrying capacity of your blood. A CBC can help diagnose conditions such as anemia, infection, inflammation, immune system disorders, and even some blood cancers.
When ordered together, a CMP and CBC provide a comprehensive snapshot of your health. They assess how well your organs are functioning, whether you have any nutritional or electrolyte imbalances, and how effectively your blood is carrying oxygen and defending against illness. These tests are often part of annual physicals and are used to investigate a wide range of symptoms, offering early clues to chronic conditions or underlying diseases.
Take The Next Step To Lasting Health
Why Consider This Test?

Optimize Your Diet
Do you wonder if you are eating a well-balanced diet? Our micronutrient testing measures the vitamins (folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin D) and minerals (iodine, zinc, and magnesium) that may be impacted by specialized diets such as vegan or vegetarian.

Identify Deficiencies
Do you wonder if you are eating a well-balanced diet? Our micronutrient testing measures the vitamins (folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin D) and minerals (iodine, zinc, and magnesium) that may be impacted by specialized diets such as vegan or vegetarian.

Monitor Levels
Do you wonder if you are eating a well-balanced diet? Our micronutrient testing measures the vitamins (folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin D) and minerals (iodine, zinc, and magnesium) that may be impacted by specialized diets such as vegan or vegetarian.
Why Functional Medicine Works Better?
Functional Medicine works better for many patients because it treats the person, not just the problem. Instead of masking symptoms with a prescription, it seeks to understand why the symptoms are happening in the first place — diving deep into root causes like inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, gut imbalances, chronic stress, or toxic exposures. This approach connects the dots between seemingly unrelated symptoms and tailors care to the individual’s genetics, lifestyle, and history. It’s proactive, not reactive — designed to restore health, not just manage disease. For patients frustrated with one-size-fits-all answers, Functional Medicine offers a path that is personalized, preventive, and deeply empowering.
In Functional Medicine, healing goes beyond pills — it’s a whole-body strategy that integrates science with lifestyle. Holistic treatment modalities may include therapeutic nutrition, personalized supplementation, advanced lab testing, gut microbiome support, detox protocols, hormone balancing, sleep optimization, and even stress-reduction techniques like meditation or breathwork. Each element is chosen based on what your body needs, not what’s trending. These modalities work together to support the body’s natural healing systems, rebalance dysfunction, and promote long-term wellness. The result is not just symptom relief — it’s transformation from the inside out.
Take the Ride and Schedule your Consultation Today!
Schedule a Consultation
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT TODAY
224.899.2000